- What is an engine
- What is a heat engine
- Classification of heat engine
- Types of engines
- Difference between the external and internal combustion engine
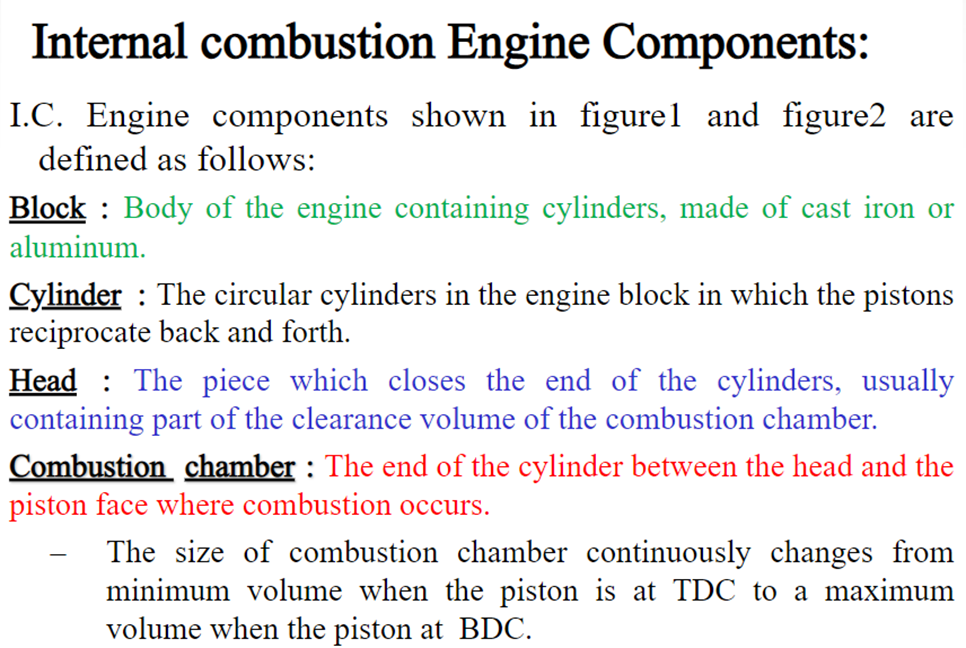
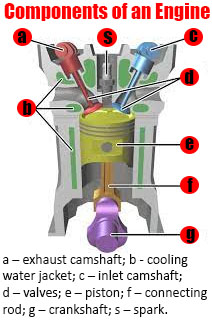
- Various components of internal combustion engine
You can also check some differences between external and internal combustion engines from the table given below:
An
internal combustion engine (ICE) is a type of heat engine that converts the energy of
fuel combustion into mechanical work. It is used in a variety of applications,
including cars, trucks, motorcycles, airplanes, and power generators.
Basic
Concepts:
- ICEs convert
the chemical energy of fuel into mechanical work.
- Fuel is mixed
with air and ignited in a combustion chamber to create a high-pressure and
high-temperature gas.
- The gas
expands and drives a piston, which is connected to a crankshaft that
converts the linear motion into rotary motion.
- ICEs require
a continuous supply of fuel and air to function.
Classification:
ICEs
are classified into two main types: spark-ignition engines (SI) and
compression-ignition engines (CI).
- SI engines,
also called gasoline engines, use a spark plug to ignite a fuel-air
mixture. They are typically used in cars and light-duty vehicles.
- CI engines,
also called diesel engines, use compression to ignite a fuel-air mixture.
They are used in heavy-duty vehicles, such as trucks and buses, as well as
in some cars and power generators.
Application: ICEs are used in a variety of applications, including:
- Transportation:
cars, trucks, motorcycles, airplanes, boats, and trains.
- Power
generation: ICEs can be used to generate electricity in stationary
applications, such as backup generators or in remote areas.
- Industrial
applications: ICEs are used in agriculture, construction, and mining,
among other industries.
Definition: An internal combustion engine is a type of heat
engine that converts the energy of fuel combustion into mechanical work. It
uses a continuous cycle of fuel intake, compression, combustion, and exhaust to
produce power.
Heat
Engine:
A
heat engine is a device that converts heat energy into mechanical work. Heat
engines are used in a wide variety of applications, including transportation,
power generation, and industrial processes. They operate on the principle of
the second law of thermodynamics, which states that heat energy naturally flows
from a higher temperature to a lower temperature.
In
a heat engine, heat is added to a working fluid (such as water, air, or a gas)
to increase its temperature and pressure. The high-pressure fluid is then used
to perform mechanical work, such as turning a turbine or a piston. The working
fluid is then cooled and returned to its original state, completing the cycle.
Heat
engines can be classified into two main types: internal combustion engines and
external combustion engines. Internal combustion engines (such as gasoline and
diesel engines) use the combustion of fuel inside the engine cylinder to create
high-pressure gas that drives a piston. External combustion engines (such as
steam engines and Stirling engines) use an external heat source (such as a fire
or a heated fluid) to heat the working fluid and create high-pressure gas that
drives a piston or a turbine.
Heat
engines are an essential part of modern technology and are used in many
applications, including cars, airplanes, power plants, and industrial
processes. Their efficiency and environmental impact are important
considerations in their design and use.
Internal
Combustion Engine vs. External Combustion Engine: An internal combustion engine is a type of heat
engine in which the combustion of fuel and air takes place inside the engine
cylinder, while an external combustion engine is a type of heat engine in which
the combustion of fuel and air takes place outside the engine cylinder.
Examples of external combustion engines include steam engines and Stirling
engines.
Here
are some key differences between internal combustion engines (ICEs) and
external combustion engines (ECEs):
Internal
Combustion Engine:
- Combustion of
fuel and air occurs inside the engine cylinder.
- Fuel and air
mixture is ignited by a spark (SI engine) or by compression (CI engine).
- The
high-pressure gas created by combustion drives a piston that is connected
to a crankshaft.
- ICEs are
typically smaller, lighter, and more compact than ECEs.
- ICEs can be
more efficient than ECEs because they can operate at higher temperatures
and pressures.
External
Combustion Engine:
- Combustion of
fuel and air occurs outside the engine cylinder, typically in a separate
combustion chamber.
- Heat from the
combustion is transferred to a working fluid, such as water or air, which
then drives a piston or turbine.
- ECEs are
typically larger and heavier than ICEs.
- ECEs are
typically less efficient than ICEs because they have lower operating
temperatures and pressures.
- Examples of
ECEs include steam engines and Stirling engines.
Overall,
the main difference between ICEs and ECEs is the location of the combustion
process. ICEs have combustion occur inside the engine cylinder, while ECEs have
combustion occur outside the engine cylinder and transfer heat to a working
fluid.
|
Internal
Combustion Engine (ICE) |
External
Combustion Engine (ECE) |
|
Combustion
of fuel and air occurs inside the engine cylinder. |
Combustion
of fuel and air occurs outside the engine cylinder, typically in a separate
combustion chamber. |
|
Fuel
and air mixture is ignited by a spark (SI engine) or by compression (CI
engine). |
Heat
from the combustion is transferred to a working fluid, such as water or air,
which then drives a piston or turbine. |
|
The
high-pressure gas created by combustion drives a piston that is connected to
a crankshaft. |
ECEs
use a working fluid to transfer heat to a piston or turbine, which then
drives a crankshaft. |
|
ICEs
are typically smaller, lighter, and more compact than ECEs. |
ECEs
are typically larger and heavier than ICEs. |
|
ICEs
can be more efficient than ECEs because they can operate at higher
temperatures and pressures. |
ECEs
are typically less efficient than ICEs because they have lower operating
temperatures and pressures. |
|
Examples
of ICEs include gasoline and diesel engines used in cars, trucks, and other
vehicles. |
Examples
of ECEs include steam engines and Stirling engines used in power generation
and other applications. |
I
hope this table helps to clarify the differences between ICEs and ECEs.
Multiple
choice questions with answers:
1.
What is a heat
engine?
A.
A device that
converts mechanical work into heat energy. B. A device that converts heat
energy into mechanical work. C. A device that converts electrical energy into mechanical
work. D. A device that converts mechanical work into electrical energy.
Answer: B
2.
What is the main
principle that heat engines operate on?
A.
The first law of
thermodynamics. B. The second law of thermodynamics. C. The law of conservation
of energy. D. The law of conservation of momentum.
Answer: B
3.
What is an
internal combustion engine?
A.
An engine that
burns fuel outside the engine cylinder. B. An engine that uses steam to drive a
piston. C. An engine that burns fuel inside the engine cylinder. D. An engine
that uses an external heat source to drive a turbine.
Answer: C
4.
What is an
external combustion engine?
A.
An engine that
burns fuel outside the engine cylinder. B. An engine that uses steam to drive a
piston. C. An engine that burns fuel inside the engine cylinder. D. An engine
that uses an external heat source to drive a turbine.
Answer: D
5.
Which type of
engine is typically smaller and lighter?
A. Internal
combustion engine. B. External combustion engine. Answer: A
6.
Which type of
engine is typically less efficient? A. Internal combustion engine. B. External
combustion engine.
Answer: B
7.
What is the most
common type of internal combustion engine used in cars? A. Gasoline engine. B.
Diesel engine. C. Steam engine. D. Stirling engine. Answer: A
8.
What is the most
common type of internal combustion engine used in trucks?
A. Gasoline engine. B. Diesel engine. C. Steam engine.
D. Stirling engine. Answer: B
9.
What is the most
common type of external combustion engine used in power generation?
A. Gasoline engine. B. Diesel engine. C. Steam engine.
D. Stirling engine. Answer: C
10. What is the working fluid used in a steam engine?
A.
Air. B. Gasoline.
C. Diesel. D. Water.
Answer: D
11. What is the working fluid used in a Stirling engine?
A.
Air. B. Gasoline.
C. Diesel. D. Water.
Answer: A
12. Which type of engine uses an external heat source to
heat the working fluid?
A.
Internal
combustion engine. B. External combustion engine.
Answer: B
13. Which type of engine uses an internal combustion
process to create high-pressure gas that drives a piston?
A.
Internal
combustion engine. B. External combustion engine.
Answer: A
14. What is the main function of a heat engine?
A.
To convert
mechanical work into heat energy. B. To convert heat energy into electrical
energy. C. To convert heat energy into mechanical work. D. To convert
electrical energy into mechanical work.
Answer: C
15. Which law of thermodynamics states that heat energy
naturally flows from a higher temperature to a lower temperature?
A.
The first law of
thermodynamics. B. The second law of thermodynamics. C. The law of conservation
of energy. D. The law of conservation of momentum.
Answer: B
I
hope these multiple choice questions and answers help to test your
understanding of the concepts related to internal combustion engines, external
combustion engines, and heat engines in general.


























20 Comments
BAK/21/CH/053
BAk/21/CH/07
Himakshi Kalita